How To Perform Merge Sort | Sorting Algorithm
In computer science, merge sort is an efficient, general-purpose, comparison-based sorting algorithm.It is a divide and conquer algorithm that was invented by John von Neumann in 1945.
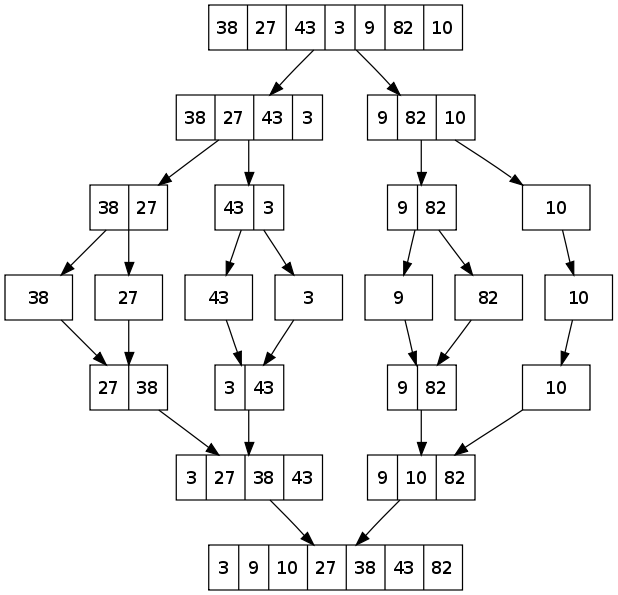
Algorithm
Conceptually, a merge sort works as follows:
- Divide the unsorted list into n sublists, each containing 1 element (a list of 1 element is considered sorted).
- Repeatedly merge sublists to produce new sorted sublists until there is only 1 sublist remaining. This will be the sorted list.
Source Code:
Download the code: Merge.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void mergesort(int a[],int low,int high)
{
int mid=(low+high)/2;
if(low<high)
{
mergesort(a,low,mid);
mergesort(a,mid+1,high);
merge(a,low,mid,high);
}
}
void merge(int a[],int low,int mid,int high)
{
int x=high-low+1;
int *b;
int i,j,k;
i=low;
j=mid+1;
k=0;
b=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*x);
while(i<=mid && j<=high)
{
if(a[i]<=a[j])
{
b[k]=a[i];
i++;
}
else
{
b[k]=a[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
if(i>mid)
{
while(j<=high)
{
b[k]=a[j];
k++;
j++;
}
}
else
{
while(i<=mid)
{
b[k]=a[i];
k++;
i++;
}
}
k=0;
for(i=low;i<=high;i++,k++)
{
a[i]=b[k];
}
free(b);
}
int main()
{
int a[]={2,4,1,5,16,9,1},i;
mergesort(a,0,6);
for(i=0;i<7;i++)
{
printf("%d",a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
#include<stdlib.h>
void mergesort(int a[],int low,int high)
{
int mid=(low+high)/2;
if(low<high)
{
mergesort(a,low,mid);
mergesort(a,mid+1,high);
merge(a,low,mid,high);
}
}
void merge(int a[],int low,int mid,int high)
{
int x=high-low+1;
int *b;
int i,j,k;
i=low;
j=mid+1;
k=0;
b=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*x);
while(i<=mid && j<=high)
{
if(a[i]<=a[j])
{
b[k]=a[i];
i++;
}
else
{
b[k]=a[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
if(i>mid)
{
while(j<=high)
{
b[k]=a[j];
k++;
j++;
}
}
else
{
while(i<=mid)
{
b[k]=a[i];
k++;
i++;
}
}
k=0;
for(i=low;i<=high;i++,k++)
{
a[i]=b[k];
}
free(b);
}
int main()
{
int a[]={2,4,1,5,16,9,1},i;
mergesort(a,0,6);
for(i=0;i<7;i++)
{
printf("%d",a[i]);
}
return 0;
}


Comments
Post a Comment